 What is the normal size of the uterus, not the pregnancy of the uterus? How many centimeters? - Quora
What is the normal size of the uterus, not the pregnancy of the uterus? How many centimeters? - QuoraThis site is intended for health professionals GP Information Links Main navigation Understand pelvic ultrasound reports To Dr. Attiya Khan and Mr. Rehan Khan 7 October 2010 Dr. Attiya Khan asked the gynecologist consultant, Mr. Rehan Khan a language guide to understand pelvic ultrasounds. How many times have you seen a report like this (see below) and thought, "What does this mean on earth?" What are the normal measurements for the uterus? How do I know when the endometrial is significantly thickened? At what point am I referring to a gynecologist? pelvic ultrasound report I have thought of this sometimes, so I decided to acquire some expert advice from an obstetrician consultant and gynecologist to find a way through the jargon. The uterus The position describes whether the uterus is anteverted (supporting forward) or retroverted (feeding backwards) or axial (inbetween). About 80% of the time the uterus is reversed and 20% of the time is reversed or axial. A reverse uterus is usually normal but if discovered in a scan it is important to correlate it with the clinical image. In patients with chronic and disparaunious pelvic pain, retroversion can be the result of chronic PID adhesions or chronic endometriosis. The size is often subjectively commented (e.g., "the uterus appears voluminous") and objectively (the diameter of the uterus). In a nulipidal woman the normal anteroposterior diameter (AP) is about 3-5 cm with a normal uterina length of about 6-10cm.1 These figures increase in women who have had children and decrease in postmenopausal women. A uterus is almost never abnormally small. The expansion of the uterin is almost always due to fibroids, and if possible, the sonographer will measure each and describe its position as submucosal (inside the cavity), subserosal (outside the cavity) or intramyometrial (inside the wall). This description is important when considered a IU or IUS because submucosal fibroids can cause a coil to be expelled. Fibroids generally do not need remission unless they are causing symptoms, such as bleeding or pressure symptoms. In addition to changes caused by fibroids, the uterus may have variable forms due to embryonic abnormalities. Clinical implications will depend on the patient's presentation, and may include menorrhagia, amenorrhoea, subfertility and recurrent abortion. Ecotexture and ecopattern describe the ultrasound appearance of the miometrium. For example, the description may be 'normal', 'suggestive of fibroid change' or 'suggestive of adenomyosis'. Endometrial The normal appearance of endometrial is smooth and regular in the face of a disturbed appearance. The appearance and thickness of the endometry varies with different stages of the menstrual cycle. The endometrial thickness is 1-4mm during menstruation, 5-7mm in the proliferative phase, up to 11mm in the periovulatory phase and 7-14mm in the secret phase. 2 Abnormal thickness can be caused by polyps, fibroids, hyperplasia and cancer. In postmenopausal women endometrials 3Ovaries As with the uterus there are subjective comments on the appearance of ovaries and then objective comments on the size, shape and ecotexture are made. The average normal size is 3.5 cm x 2.5cm x 1.5cm. After menopause ovaries usually measure 2cm x 1.5cm x 1cm or less. There may be cysts present in the ovaries. These may include follicular cysts, luteum body cysts, hemorrhagic cysts, endometriomas, simple cysts and polycetic ovaries that appear. Cytos nе5cm will need forward derivation as they are associated with a greater probability of ovarian cyst accident. Symptom cysts in premenopausal women also deserve to be referred. In the postmenopausal woman, any new cyst needs remission to exclude malignity. It is reassuring if the ovaries cannot be seen in the scan as this excludes the pathology. Tubercles are not usually seen - if observed there is usually pathology, such as hydrosalpinx. The DouglasFluid bag in the Douglas bag can be measured. Its presence is generally physiological of a broken follicular cyst, but it may also be associated with a broken ovarian cyst or PID. References1. Eberhard Merz. Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Vol. 2. Second edition, Thieme, Texas, 1997.2. Goldberg BB, McGahan JP. Atlas of ultrasound measurements. Elsevier Health Sciences, Philadelphia 2006.3.SIGN. Research of postmenopausal bleeding. Guide SIGN 61, 2002.GP Online recommends Share this article Read these below Have you registered with us yet? Register now to enjoy more free email articles and newsletters The voice of today's GP. News, ideas and clinical education. Stay signed in Only published One in six doctors says that local vaccination sites have been forced to reorganize sessions... The government plans to increase the salary of NHS staff by only 1% by 2021/22 will damage the patient... As real world data on the impact of Pfizer/BioNTech and Oxford/AstraZenca... Dr. Pipin Singh summarizes the recognition and initial management of... GPs across the UK are playing a leading role in the largest... The BMA has suspended the vote in part of its GP committee election while investigating...
GoogleI'm sorry... Google Sorry... but your computer or network can send automated queries. To protect our users, we cannot process your request right now.
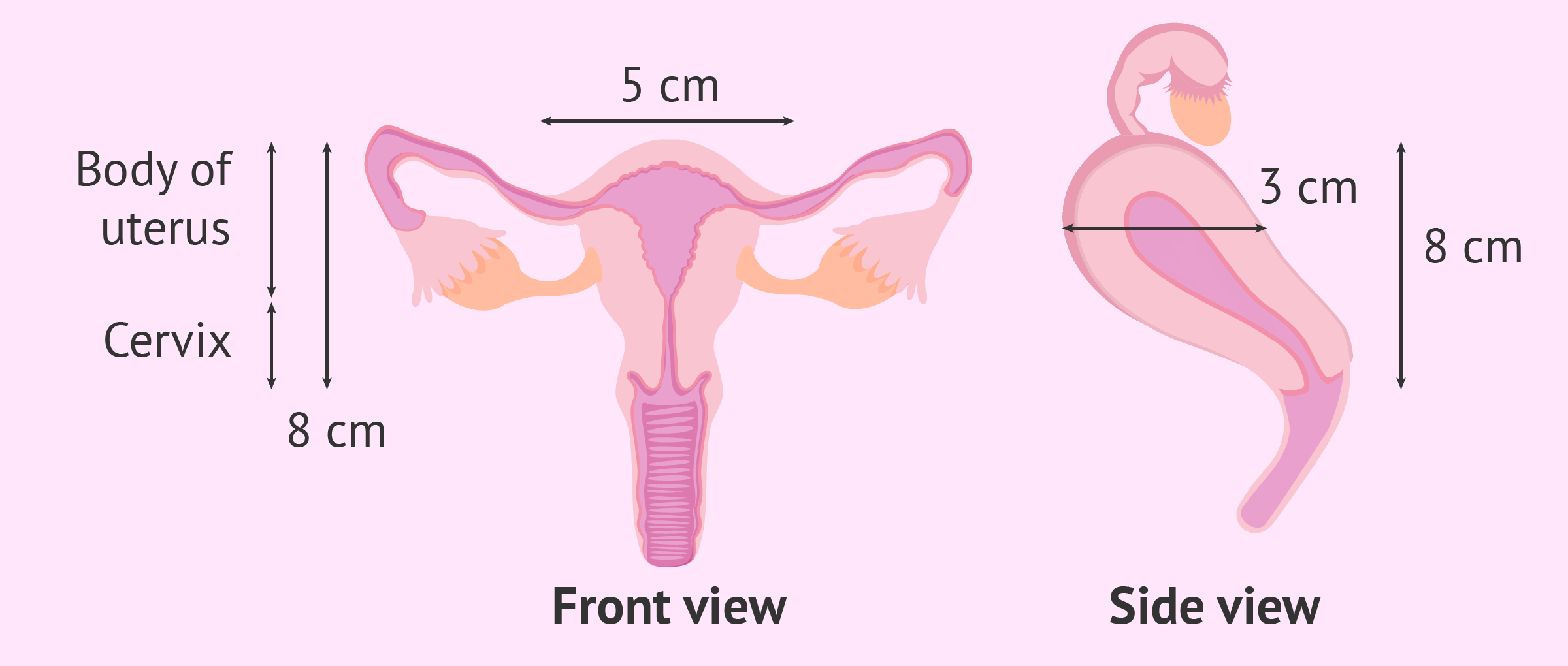
Normal size of the uterus
Sonographic measurement of uterine dimensions in healthy nulliparous adults in Northwestern Nigeria Umar UM, Isyaku K, Adamu YM, Abubakar S A, Kabo N A, Nura I, Naimatu A T - Sahel Med J
Uterus | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
normal uterus size chart - Yerse
Endometrium - Wikipedia
Pelvic ultrasonography in children and teenagers
Uterus | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
Table 2 from Normal uterine size in women of reproductive age in northern Islamic Republic of Iran. | Semantic Scholar
normal uterus size chart - Yerse
Sonographic measurement of uterine dimensions in healthy nulliparous adults in Northwestern Nigeria Umar UM, Isyaku K, Adamu YM, Abubakar S A, Kabo N A, Nura I, Naimatu A T - Sahel Med J
Uterus in Pregnancy - Functions, Position, Size & more
Normative data for uterine size according to age and gravidity and possible role of the classical golden ratio - Verguts - 2013 - Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology - Wiley Online Library
A photograph (A-c.2) showing the difference in the size of the gravid... | Download Scientific Diagram
Imaging of the Female Pelvis through the Life Cycle | RadioGraphics
normal uterus ultrasound how to
The Normal Uterus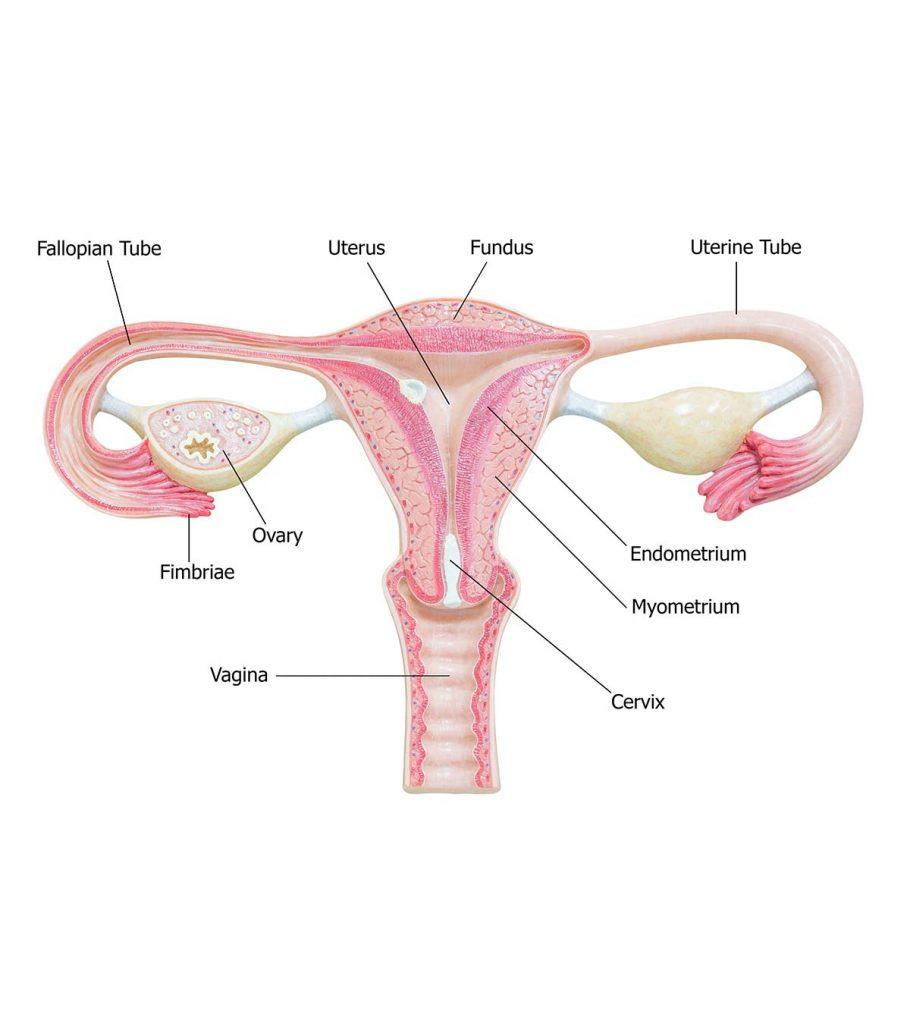
Normal Thickness Of Endometrium, Thickening Symptoms & Causes
The Normal Uterus
US of the Pediatric Female Pelvis: A Clinical Perspective | RadioGraphics
The Radiology Assistant : Normal Values - Ultrasound
What is Bulky Uterus? It's Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Uterine Polyps: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
A photograph (A-c.2) showing the difference in the size of the gravid... | Download Scientific Diagram
Endometrial Thickness: What's the Normal Range for Conceiving?
Profile of uterine size | Download Table
Enlarged uterus: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Sono 202 normal gyn anatomy
The Normal Uterus
normal uterus ultrasound how to
Uterus in Pregnancy - Functions, Position, Size & more
Does a Uterus Really Double in Size During Menstruation?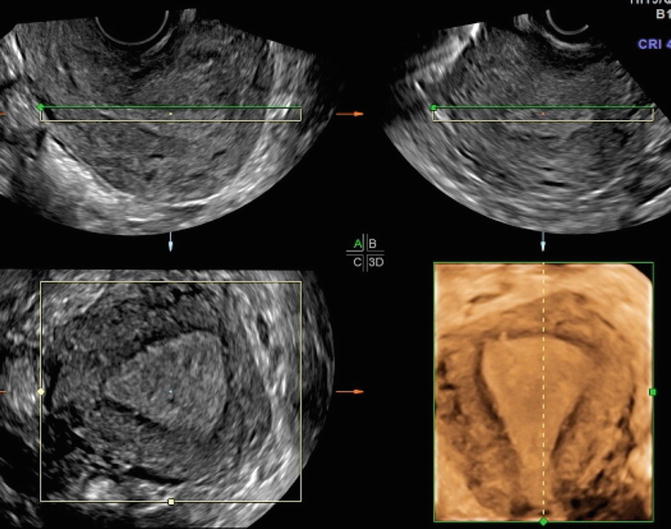
The Normal Uterus | Radiology Key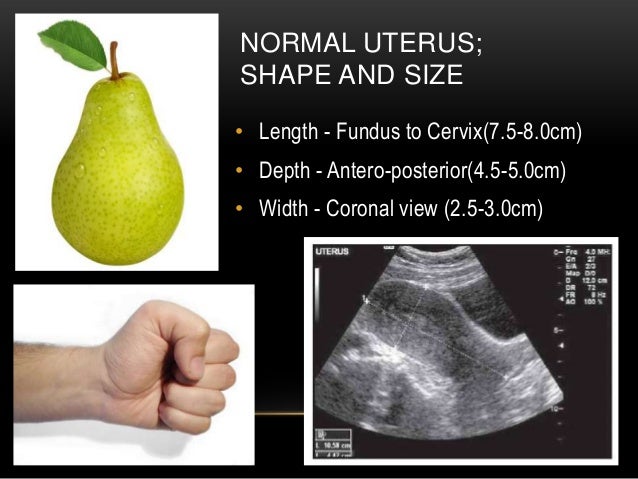
Basic gynae ultrasound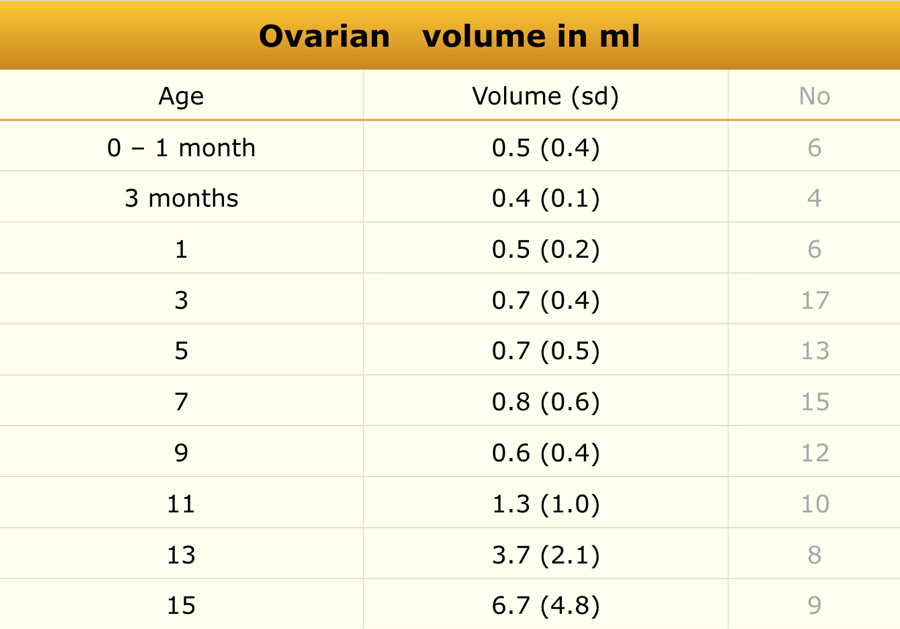
The Radiology Assistant : Normal Values - Ultrasound
PDF) Measuring the length of endometrial cavity; Comparison of a new marked flexible disposable uterine sound and metal uterine sound with ultrasonography
Uterus - Wikipedia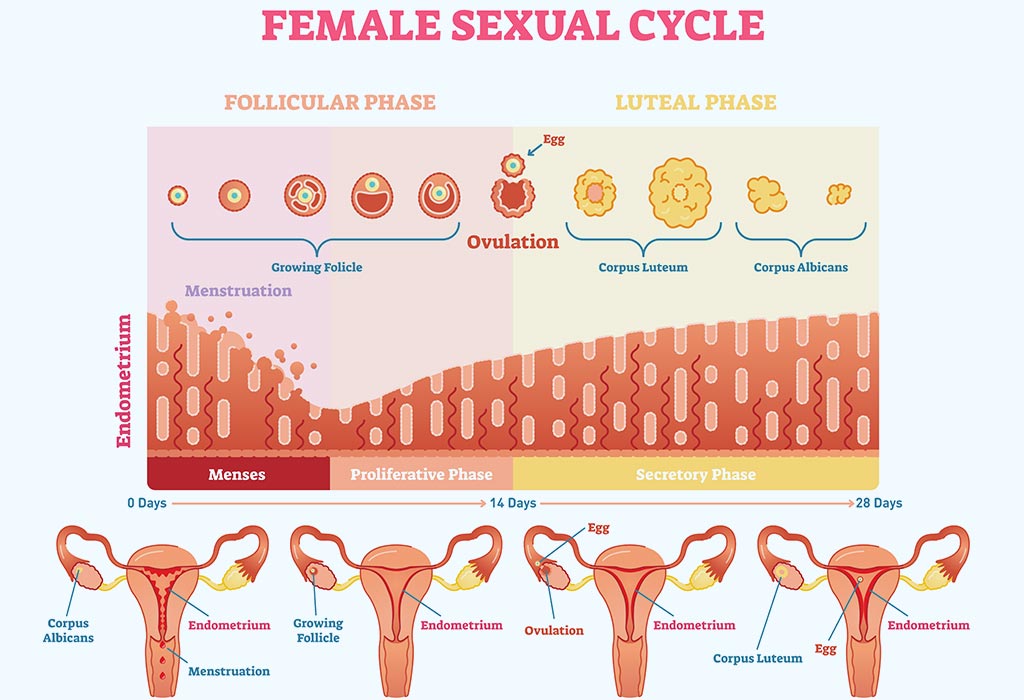
Endometrial Thickness: What's the Normal Range for Conceiving?
PLOS ONE: A Validated Normative Model for Human Uterine Volume from Birth to Age 40 Years
Pediatric Radiology Normal Measurements | OHSU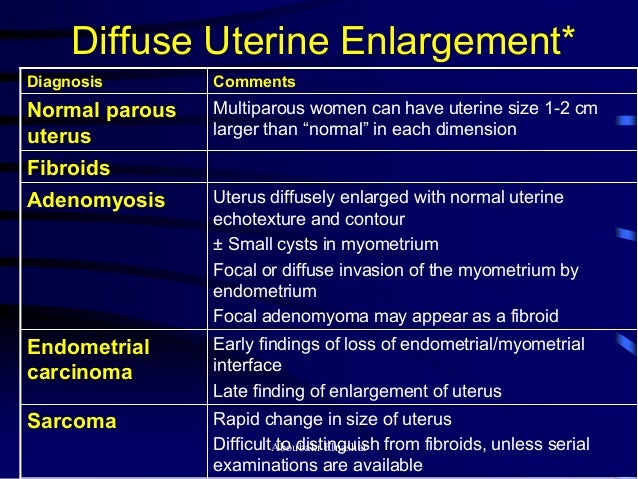
Ultrasonography of the uterus


































Posting Komentar untuk "normal measurement of uterus"